Recording, Mixing and Mastering
Published on 15/12/2021

In some of our previous posts we have been dealing with music for pictures from the composition point of view.
In this one we shall talk a bit about a technology that is finding great success in the audio production community, namely: Dolby Atmos Music
We started to hear about immersive music since quadriphony and related Pink Floyd esperiments.
Several attempt since then have been tried with a certain degree of success in cinema, videogames and home theaters.
It is quite a while that we are hearing about Dolby Atmos. Atmos is a technology developed by Dolby Laboratories to give to the the listener the experience of being embedded into the sonic ambient as he/she would be in the real world.
The main feature of Atmos is that it is possible to enjoy the full experience even in environments not specifically tuned such as a cinema hall or a tuned mixing room. One can listen and appreciate the details even in places such as the car or at home.
Atmos has been presented in 2012. The system can comprise up to 64 discrete channels to give the listener a precision never achieved before. The music related application are quite new yet promising.
Dolby has recently defined the specs for Dolby Atmos Music rooms to allow production and mixing with this technology.
Two are the main features of the system. Spacial precision is the first. The sound sources are precisely localized ain the 3D field.
The second one is the capability of allowing the listener to feel the same experience independently by the listenig equipment he/she is using. This feature is known as scalability.
With the other immersive techniques the experience is correct only if the listening system and the environment is similar to the one used to produce the music.
In cinema the problem has been solved by strictly defining the specification of the listening rooms and the speaker systems. This approach has the limitation that in other environments such as, for instance, the home theaters the experience remains different and of lower quality.
Atmos offers a sonic result never given before with the big advantage of being compatible with different listening equipments.
The proper perception of a given source in the space depends by many factors. A lot of time and effort have been spent by researchers to determine the correct equalizations during the mix phase also considering that sound sources can be even moving in the scene.
With the traditional systems is the sound engineer skill to make the difference. With Dolby Atmos Music we get a standardized set of features and functions to simplify operations. This is possible thanks to a processor responsible for the decodification and rendering of the sonic messages. This processor is also taking care of the scalability.
The Dolby Atmos Music master is a set of data flows composed by Beds, Objectsand meta-data.
Beds can be though as audio stems in several formats (7.1 or 9.1 or 7.1.2 for instance).
When we talk about formats the first number is for the speakers around the listener, the second is for the number of Low Frequency Effect (LFE) devices and the third for the channels on the ceiling.
The Objects are sound sources to whom the spacial coordinates (meta-data) are linked to precisely indicate the position in the 3D space.
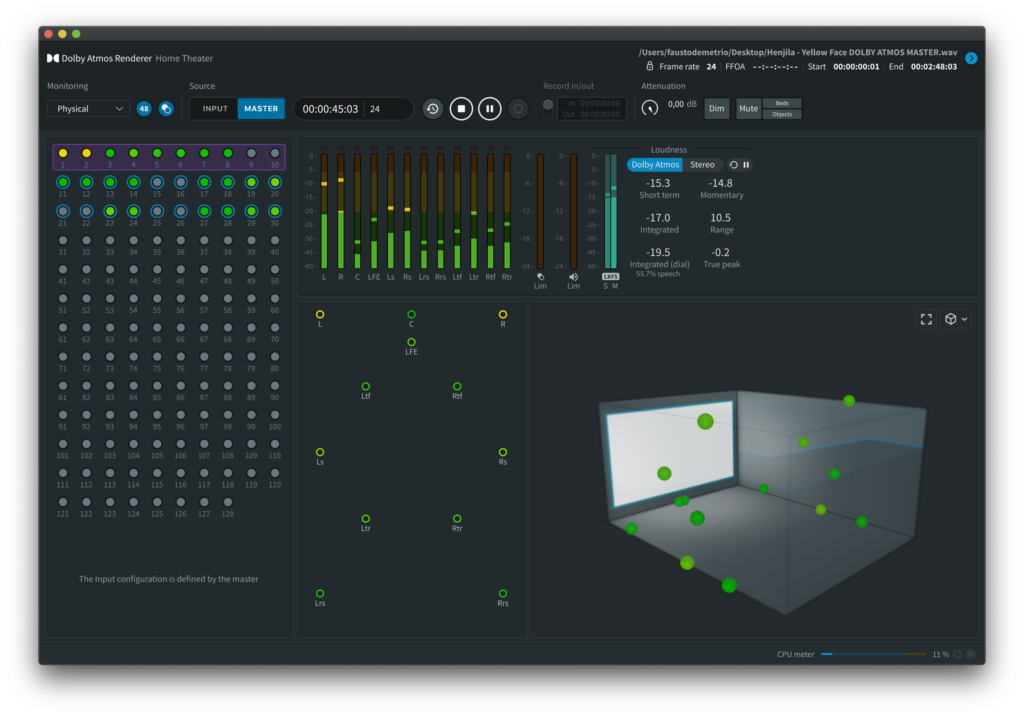
A Dolby Atmos Music master is capable of including up to 128 objects at 48 KHz, 24 bit. The Objects, and related meta-data, are the biggest innovation of the system.
A mix made in a 9.1.6 room can be plaied with the same precision either in a 7.1.4 room or in a cinema with more speakers because the meta-data linked to the Object (processed by a specific renderer) will place the source in the right 3D spacial position.
After many years of experience for cinema, Dolby defined new specs for Home Entertainment first and than for the music world by defining Dolby Atmos Music.
The Dolby Atmos Music rooms must have precise featurse. Among those:
There are also specific ranges about room dimensions and room audio response.
There is no “Dolby certification” for mixing room as it was for cinema and home entertainment systems. The studios which are compliant with the spec are listed in dedicated pages at the Dolby Music web site.
Mixing room standardization is a key factor to maintain the coherence from production to listening. The main configuration for the listed mixing room is the 7.1.4.
The Dolby decoder allows for precise colocation of the objects. Specfic further processing can be applied by the manufactorers of listening systems of by the music distributors.
Headphone listening is one of the possible targets for the Dolby Atmos Music renderer.
With no processing the headphone perception places the sounds in the axes betweet the ears or above the head. By applying the Dolby Atmos algorythms the spacial sensation enourmosly improves but doesn't reach the complexity achievable with a full speaker configuration.
Listening experience can also depend by further processing applied by distributors.
By the Dolby renderer it is possible to have a preview of the sound proposed by Tidal or Amazon. It will not be possible to have the same for Apple Music because of the further processing applied by this company.
This is the reason why you need a well specified room to be shure that the music message will be coherent among the various distribution platforms.
It is better not to mix via headphones or soundbars.
On the opposite, if the mix sounds good in a well set up room, the result will be coherent in all other listening scenarios.
Dolby Atmos Music is the biggest revolution happened since the advent of digital technology.
24 bit listening finally allows for the catching up of all details and, for the first time, a given source is placed in the right place in the 3D space.
Mixing techniques will probably have to be adapted to this new scenario but the road to the future is now clear and well defined. Stay with us for our deepening about this topic!
Join us today and get 5% off your next order!

Empty cart